Enterprise IT Skill Frameworks
Contents
1 Competency Frameworks
The emphasis on competence has become international as Enterprise IT and ICT in general have become indispensible across the globe. They derive from a growing understanding of the need for a common language for competences, knowledge, skills and proficiency levels that can be understood across national borders. A common framework enables the identification of skills and competences that may be required to successfully perform duties and fulfill responsibilities in an EIT workplace. They provide a common basis for the selection and recruitment of EIT staff, as well as forming the basis for employment agreements, professional development plans, and performance evaluation for ICT professionals.
Many national and regional governments have come to require certification of EIT practitioners. Accordingly, they have had to develop their own definitions of ICT competences. Given the increasingly international composition of the EIT workforce, the EITBOK has included information from 3 major frameworks that are emerging as inter-regional. In general, these frameworks work towards a common understanding of competence, defined by the e-CF, for example, as “demonstrated ability to apply knowledge, skills and attitudes to achieve observable results."
Creating mappings between these frameworks and our chapters is challenging, because they come from different perspectives and have different goals. There is rarely a 100% correspondence between the frameworks and our chapters, and, despite careful consideration some subjectivity was used to create the mappings. Please take that in consideration as you review them.
2 Skills Framework for the Information Age
SFIA has been used for some 26 years and developed using a collaborative approach. The internationally represented SFIA Council oversees the direction of development for the not-for-profit SFIA Foundation, which owns and regularly updates the framework, using a well-established open process, for the benefit of the IT industry and IT professionals. The SFIA Framework has been translated in to 6 languages (English, Spanish, German, Arabic, Japanese and Chinese with more languages scheduled including French and French Canadian). It has been downloaded and used by organizations and individuals in nearly 180 countries. It can be downloaded for free at www.sfia-online.org.
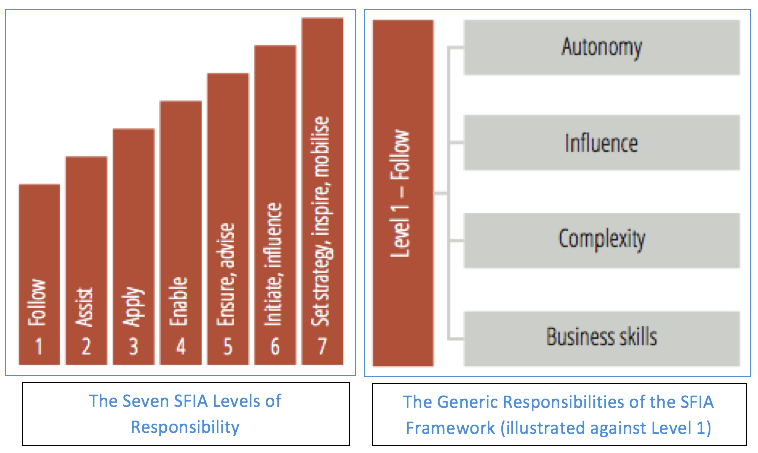
The SFIA Framework identifies 97 professional skills across IT and supporting areas and 7 levels of responsibility. The 7 levels in the SFIA Framework are used to provide generic levels of responsibility and to reflect experience and competency. The SFIA Framework is based on demonstrated ability of applying a skill at a particular level, employing professional and behavioural skills as well as knowledge. The definitions describe the behaviors, values, knowledge and characteristics that an individual should have in order to be considered competent at a particular level. Underlying each SFIA Level are generic responsibilities of Autonomy, Complexity, Influence and Business Skills. These are described at each SFIA Level.
Figure 1. SFIA Levels of Responsibility
The 97 IT skills of the SFIA Framework are grouped into categories and sub-categories, a skill has a name, a code, a skill description and a level description (for that skill at each level practiced).
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| General Responsibilities | The generic responsibility attributes delineated for all skills at all SFIA Levels:
|
| Skill Category | A logical grouping of the skills for the purposes of navigation. These categories are further broken down into sub-categories. |
| Skill Name | The name of the skill |
| Skill Description | A description of what the skill is without reference to the levels practiced |
| Level Descriptors | A description of the skill for each of the levels practiced, phrased to facilitate their use as professional competencies.
|
3 European Competency Framework
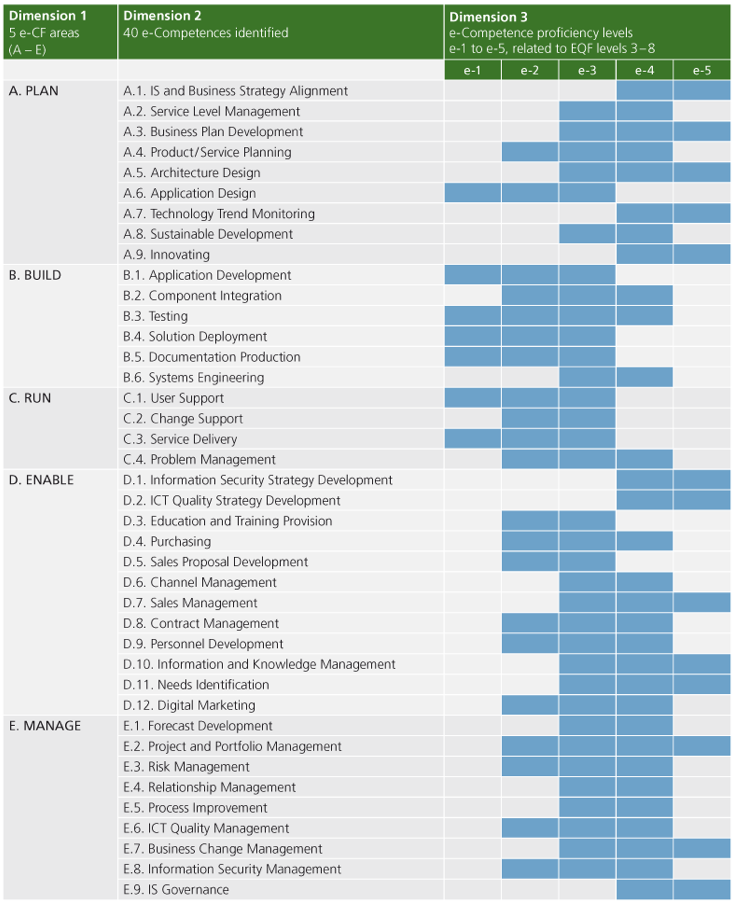
The European e-Competence Framework (e-CF) from the European Union provides a reference of 40 competences required for performance in the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) workplace, using a common language for competences, knowledge, skills and proficiency levels that can be understood across Europe. The use of the e-CF by companies and organisations throughout Europe supports the transparency, mobility and efficiency of ICT sector related human resources planning and development.
As the first sector-specific implementation of the European Qualifications Framework (EQF), the e-CF can be used by ICT service, demand and supply organizations, and by managers and HR departments, for education institutions and training bodies, including higher education, by professional associations, trade unions, market analysts and policy makers, and other organisations and parties in public and private sectors. The structure of the framework is based on four dimensions:
| Dimension 1 | 5 e-Competence areas, derived from the ICT business macro-processes PLAN – BUILD – RUN – ENABLE – MANAGE. Main aim of dimension 1 is to facilitate navigation through the framework |
| Dimension 2 | A set of reference e-Competences for each area, with a generic description for each competence. 40 competences identified in total provide the European generic reference definitions of the framework. |
| Dimension 3 | Proficiency levels of each e-Competence provide European reference level specifications on e-Competence levels e-1 to e-5, which are related to EQF levels 3-8. |
| Dimension 4 | Samples of knowledge and skills relate to e-Competences in dimension 2. They are provided to add value and context and are not intended to be exhaustive. |
There are five e-CF proficiency levels, e-1 to e-5, which relate to EQF learning levels 3 to 8. For a description of the EQF levels, please see https://ec.europa.eu/ploteus/en/content/descriptors-page.
| e-Competence Level | EQF Level |
|---|---|
| 5 (highest) | 8 |
| 4 | 7 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 2 | 4 and 5 |
| 1 | 3 |
As in SFIA, not all skills are subject to all 5 levels. The following table shows the spread of competency levels for each skill.
Figure 3. The European Competency Framework Overview
4 The i Competency Dictionary
The i Competency Dictionary (iCD) was developed and is maintained by the Information Technology Promotion Agency (IPA) in Japan. It consists of a comprehensive Task Dictionary and a corresponding Skill Dictionary. The Task Dictionary contains all the tasks that EIT outsourcers or EIT departments are expected to accomplish, while the corresponding Skill Dictionary provides the skills required to perform those tasks.
The diagrams below show how the task and skill dictionaries are structured to be used together. The skills needed to become competent at each task are enumerated in a Task vs. Skill table. In each of the EITBOK chapters, we have shown one of the relevant tasks (at Task layer 2), along with its prerequisite skills from layers 2-4. In the diagrams below, we have indicated the number of tasks and skills that are included in the full iCD. The complete iCD Task Dictionary (Layers 1-4) and Skill Dictionary (Layers 1-4) can be obtained by returning the request form provided from: http://www.ipa.go.jp/english/humandev/icd.html
Note that the IPA is also responsible for the Information Technology Engineers Examination (ITEE), which has grown into one of the largest scale national examinations in Japan, with approximately 600,000 applicants each year.
4.1 Task Dictionary
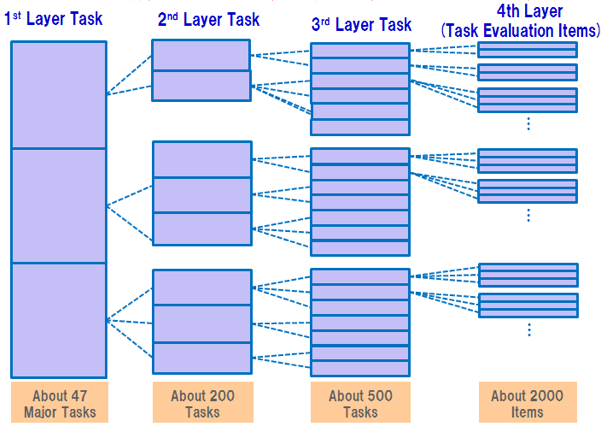
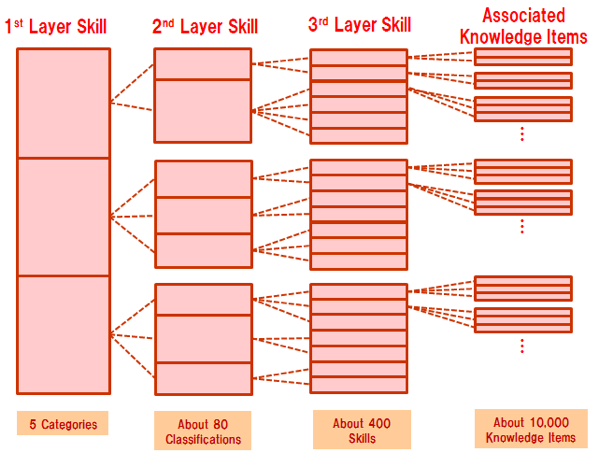
The Task Dictionary is intended to be used and applied by companies and organizations to determine tasks in line with their business strategies or business plans. Tasks are used to define their organizational functions and the roles of personnel. The structure of the dictionary assumes a wide range of corporate activities, so that companies with any kind of business model can use and apply it. The Task Dictionary is comprised of four layers that are divided into three task layers plus the Task Evaluation Items layer (approx. 2,000 items).
Figure 4. The iCD Task Dictionary Structure
4.2 Task Dictionary Chart
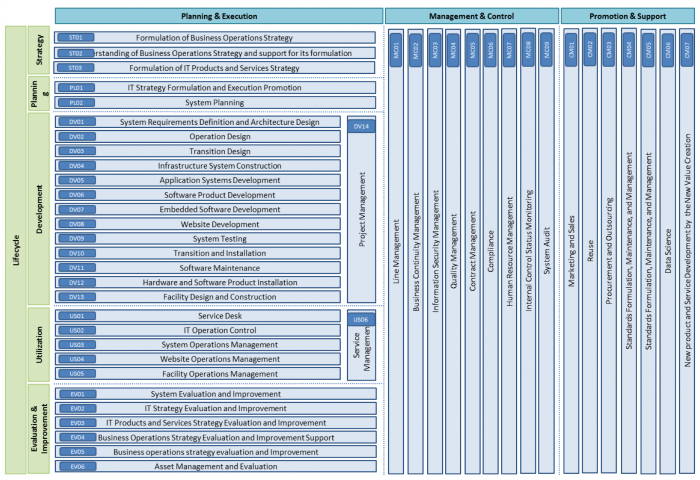
The Task Dictionary Chart can be used to obtain a bird’s-eye view of the entire Task Dictionary on the 1st Layer Task level. This chart represents a task structure composed of the business lifecycle as vertical line (strategy, planning, development, utilization, evaluation/improvement) and tasks associated with entire lifecycle as horizontal line (Management/Control, and Promotion/Support).
Figure 5. The iCD Task Dictionary Chart
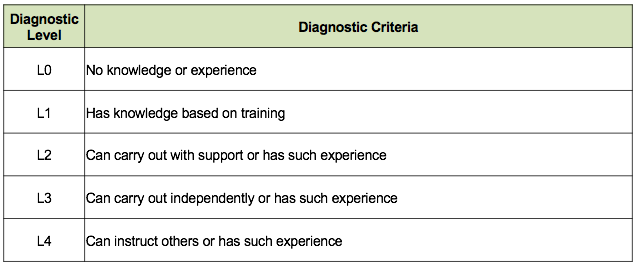
4.3 Examples of Task Evaluation Diagnostic Level and Criteria
This table is intended to define the task diagnostic level and Criteria. Diagnostic Criteria can be applied to task evaluation items or appropriate layer tasks to evaluate one’s task performance capability. The levels are from L0 to L4. This Diagnostic Criteria can be applied to individuals and the total task performance capability is manipulated for each department by aggregating all department members result.
Figure 6. Examples of Task Evaluation Diagnostic Level and Criteria
4.4 Skill Dictionary
Skills are capabilities required to handle associated knowledge items to execute a task. The Skill Dictionary is comprised of four layers divided into three skill layers plus Associated Knowledge Items (approx. 10,000 knowledge items). The Skill Dictionary refers and sorts the items from the major Body of Knowledges/processes and skill standards in the world.
Figure 7. The iCD Skill Dictionary Structure
4.5 Skill Dictionary Chart
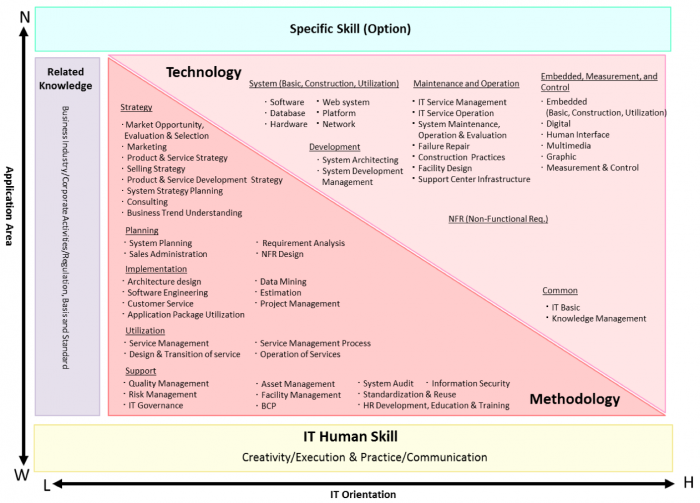
The Skill Dictionary Chart can be used to obtain a bird’s-eye view of the entire Skill Dictionary on the 1st and 2nd skill layers. The Skill Dictionary is divided into five categories based on the skill characteristics: methodology, technology, related knowledge, IT human skills, and specific skill (optional). This chart represents a skill structure on the perspectives of the IT orientation (Horizontal line: High-Low) and the application area (Vertical line: Wide-Narrow).
Figure 8. The iCD Skill Dictionary Chart
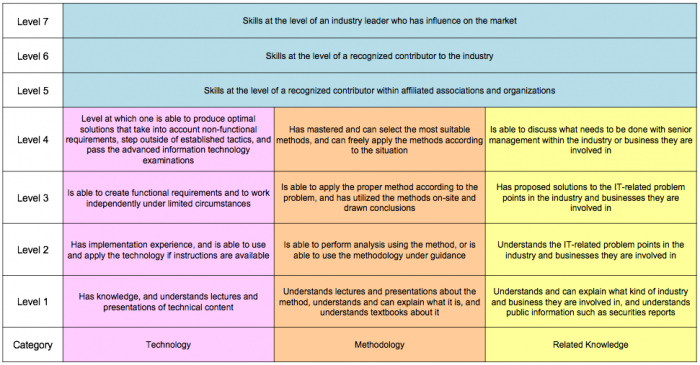
4.6 Skill Proficiency Level
This chart measures the skill proficiency level using seven levels of skill proficiency criteria. Level 1 to 4 criteria differs according to contents of technology/methodology/related knowledge. Skill proficiency level 4 is the highest acquisition level of the skill for the task accomplishment. Level 5 to 7 criteria is defined across the categories to evaluate by social contribution degree as a professional.
Figure 9. Skill Proficiency Level
4.7 Task Versus Skill Table
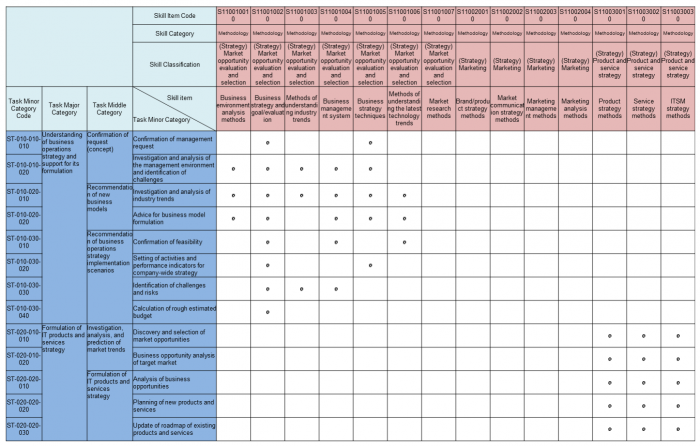
Table 10 indicates with a dot in the related cell those skills that are associated with particular tasks. Displayed below is just a small portion of the complete table. This table is used to identify the skills corresponding to each task and vice versa.
Figure 10. Task Versus Skill Table (extracted)
5 The IEEE Software Engineering Competency Model
The software engineering competency model (SWECOM) describes competencies for software engineers who participate in development of and modifications to software-intensive systems. Skill areas, skills within skill areas, and work activities for each skill are specified. Activities are specified at five levels of increasing competency. Case studies of how the SWECOM model can be used by a manager, an employee, a new hire, or a curriculum designer are provided. Staffing Gap Analysis and Individual Gap Analysis worksheets are included in an appendix.
Individuals may download the SWECOM document here: https://www.computer.org/web/peb/swecom-download
6 The U.S. 2012 Clinger-Cohen Core Competencies and Learning Objectives
The Clinger-Cohen Core Competencies reflect a core body of 12 competency areas identified by the Federal CIO Council of the United States as fundamental to the effective management of federal technology resources:
- Policy and Organization
- Leadership and Human Capital Management
- Process and Change Management
- Information Resources Strategy and Planning
- IT Performance Assessment: Models and Methods
- IT Project and Program Management
- Capital Planning and Investment Control
- Acquisition
- Information and Knowledge Management
- Cybersecurity/Information Assurance
- Enterprise Architecture
- Technology Management and Assessment . Each of the 12 competency areas has several subordinate competencies and all subordinate competencies have associated learning objectives.