Enterprise Architecture
Note: This wiki is a work in progress, and may contain missing content, errors, or duplication.
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Goals and Principles
- 3 Context Diagram
- 4 What is Enterprise Architecture?
- 5 A Brief History of Enterprise Architecture
- 6 The Purpose and Value of Enterprise Architecture
- 7 The Conventional Wisdom
- 8 The Geography of Enterprise IT Architecture and Links to Other Disciplines
- 9 Summary
- 10 Key Skills
- 11 Roles
- 12 Standards
- 13 References
- 14 Additional Reading
1 Introduction
Enterprise architecture (EA) is the practice of conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation using a holistic approach for the successful development and execution of strategy. EA applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their organization’s strategies.
Like many other disciplines, EA is evolving. [1] The EA concept dates back to the late 1980s as a response to the increased complexity associated with the introduction of distributed computing. For the first time, the unmanaged and uncontrolled replication of systems providing similar capabilities, as well as the same or very similar data sets were springing up around the enterprise. The result was increased difficulty in integrating and evolving systems to address changing business needs. The initial EA concept was to adopt an enterprise-wide view of an organization’s computing resources. By developing and applying standards and governance throughout the organization, unnecessary complexity and redundancy could be avoided.
EA provides this enterprise-wide view. Although it was initially motivated by the need to control EIT expense, EA is now also driven by the need for improved IT innovation, effectiveness, and efficiency in a rapidly changing business and technology environment. If done well, an organization’s enterprise architecture provides context for all the enterprise’s IT activities.
While there are a number of frameworks, practices, and approaches for EA, there is a generally accepted body of conventional wisdom on the subject, and this chapter introduces the basic concepts.
2 Goals and Principles
- To assure that models of the enterprise are accurate and kept current
- To provide artifacts such as requirements, specifications, guiding principles, and conceptual modes that describe the next stage of evolution of an organization, often called the future state or to be state.
- To provide the holistic information and insights to identify opportunities to execute on the enterprise strategy and make better informed decisions.
- To create a collaborative bridge between the needs of the organization and the support provided by EIT, rather than dictating to either side.
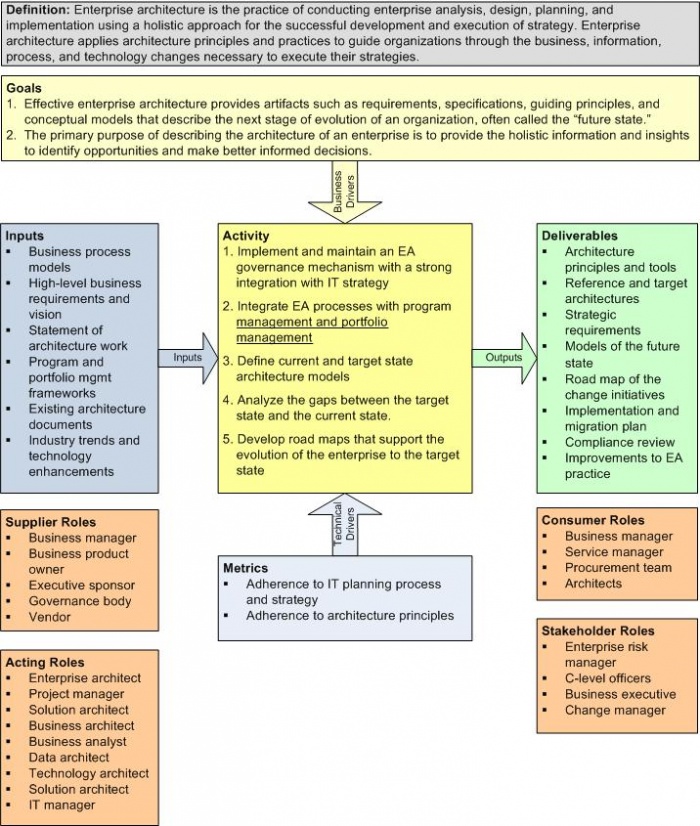
3 Context Diagram
Figure 1. Context Diagram for Enterprise Architecture
4 What is Enterprise Architecture?
4.1 The Concept of Enterprise
The first definition listed in a dictionary for enterprise is generally some variation on the concept of an ambitious endeavor or undertaking. Subsequent definitions define it as the entity (typically an organization) that carries out such an undertaking. This latter definition is the common understanding of the meaning of enterprise within the EA community. More specifically, it is an entity that can be reasonably well modeled as comprising the business and EIT, including such organizations as governments and nonprofits within its compass.
4.2 The Concept of Architecture
The formal definition of architecture cited most frequently by the EA community is the definition from ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010:2011:
“... “architecture” means whatever the framework being used (explicitly or implicitly) implies it is by the various architectural representations it recommends for use. ” [2]
4.3 A Definition of Enterprise Architecture
The Federation for Enterprise Architecture Professional Organizations (FEAPO) defines EA as follows:
“Enterprise architecture is a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a holistic approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. Enterprise architecture applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their strategies. These practices utilize the various aspects of an enterprise to identify, motivate, and achieve these changes.” [3]
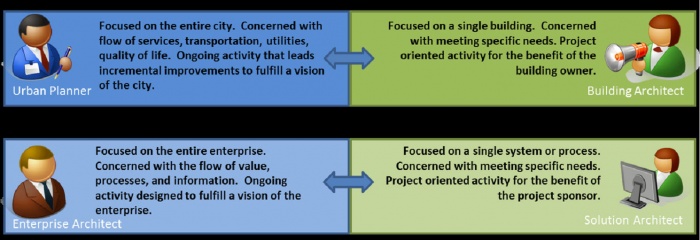
Analogies between enterprise architecture and urban planning have been made, because both define common guidelines, standards, and frameworks with which solution architects and building architects, respectively, must comply (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Urban Planner and Enterprise Architect versus Building Architect and Solution Architect [3]
5 A Brief History of Enterprise Architecture
The need for enterprise architecture arose for two separate reasons. The first reason was driven by technology. The arrival of distributed computing in the 1980s resulted in increased IT complexity due to additional scale, diversity, and connectivity in the computing environment. The additional complexity lead to significantly higher EIT development, support, and operational costs. With rising costs came pressure from management to slow the growth of EIT budgets and increase the business effectiveness of EIT support. Directives to “do more with less” and unrelenting pressure to increase efficiency and effectiveness required new approaches to EIT strategy. To some extent, consolidation, standardization, and commoditization worked as EIT expense reduction strategies; however, there were limits to their effectiveness, because they still lacked a holistic and systematic understanding of the connectedness between business roles and processes, information data elements and flows, supporting application systems, and underlying technology infrastructure.
The second motivation for EA was business-driven, due to the ever-increasing pace of external change combined with the difficulty for many organizations to successfully execute their business strategies. Michael Porter estimates that more than 80 percent of organizations fail to execute their business strategies, and ineffective execution was the reason for failure for more than 70 percent of them. [4] The principles and practices in EA help enterprise managers move their organizations from where they are to where they want them to be.
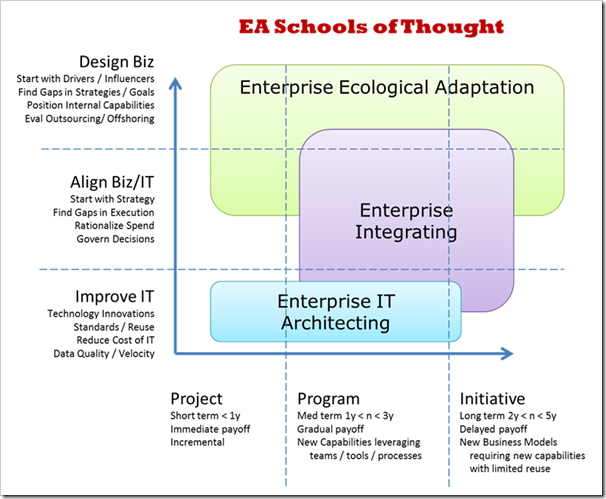
Based on whether one views EA solely for technology-based or business strategy-based reasons, the scope of EA, including its concerns, assumptions, and limitations varies. One of the most cogent analyses of the range of EA definitions was presented by James Lapalme, who describes three schools of thoughts on EA: [5]
- Enterprise-wide IT platform (effective enterprise strategy execution and operation through EIT-business alignment)
- Enterprise (effective enterprise strategy implementation through execution coherency)
- Enterprise-in-environment (innovation and adaptation through organizational learning)
Nick Malik builds on Lapalme’s three schools, and describes three categories of EA application: [6]
- Enterprise IT architecting
- Enterprise integrating
- Enterprise ecological adaptation
These differences between these categories vis depicted graphically in Figure 3.
Figure 3. EA Schools of Thought [6]
EA can serve a number of different goals (the vertical axis of Figure 3) and can provide direction and support for a range of time horizons and enterprise value (the horizontal axis). It is important to distinguish the type of EA that an organization needs and wants to establish. By doing so, the boundaries and handoffs between EA and business executives in the execution of their business strategy, as well as between EA and EIT governance and strategy, are clear. Without that clarity, ongoing confusion and issues with collaboration and alignment will likely be created.
Regardless of the school of thought, a framework for EA is needed to describe the interconnectedness of the business, information, systems, and technology elements (often called artifacts). In 1987, John Zachman published what is commonly viewed as the first framework describing a classification scheme for artifacts at several levels of abstraction. [7] In the 1990s, a reference model was developed for EA by and for the US Department of Defense (DoD) called the Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM).
In 1995, based on TAFIM, The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) had its first release. Since then, TOGAF has evolved and released TOGAF 9.1 in 2011. It maintains that “a complete EA description should contain all four architecture domains (business, data, application, technology), but the realities of resource and time constraints often mean there is not enough time, funding, or resources to build a top-down, all-inclusive architecture description encompassing all four architecture domains, even if the enterprise scope is ... less than the full extent of the overall enterprise.” [9]
While TOGAF may be the most popular EA framework (based on published certification numbers), there are many different frameworks available. Generally, they fall into these types: consortia-developed (e.g., TOGAF), defense industry (e.g., DODAF (U.S.)), government (e.g., E-overheid NORA (Dutch), open-source (e.g., MEGAF), and proprietary (e.g., Capgemini’s IAF). [10]
6 The Purpose and Value of Enterprise Architecture
As noted in the Introduction, the driving force behind enterprise architecture has changed since its initial appearance. Four purposes or value propositions for EA are frequently given:
- Manage, if not master complexity
- Ensure business/EIT alignment
- Facilitate successful organizational change, transformation, and agility
- Bridge strategy and execution
A common comparison is with city planning, where EA maintains the “master plan” for the enterprise’s business/technology integration.
6.1 Manage Complexity
The elimination of unnecessary complexity was the earliest justification for EA. Eliminating complexity makes systems easier to understand, easier to control, and, therefore, less expensive to develop, operate, and maintain within the EIT function. In a large organization with multiple units, different systems and business processes often start at different times or in different geographies. For example, an organization might have multiple human resource (HR) systems, overlapping sales forecasting systems, or disconnected procurement systems. An EA-based framework and roadmap supports the elimination of redundancy and the integration of systems and data.
6.2 Alignment
In an effort to speak the language of the enterprise's business, the complexity reduction rationale fell into disuse as the EA community shifted its focus of the value proposition for EA to business/EIT alignment. The alignment rationale has become increasingly widespread, and remains the dominant value model for EA.
Examples of alignment activities include mapping business roles and processes to information data flows and the underlying EIT systems and technology which support them.
6.3 Change, Transformation, and Agility
Another motivation for EA has been as the presumed enabler of transformation, via agility. The idea is that in a business and technology environment of continuous rapid change, only organizations that can anticipate and respond appropriately and quickly to such change can survive. EA is offered as the means for an organization to do so. The assumption is that changes in the business environment require “disruptive” changes in the (information) technology environment, and thus a strategically agile EIT function confers that agility on the organization as a whole. Disruptive changes also occur when an enterprise becomes part of an acquisition or merger. This can go both ways. For example, when Twitter appeared, the business wanted to use it so it disrupted EIT instead of EIT disrupting the business. Based on this important symbiotic relationship between the enterprise and EIT, it is particularly important for both to be agile and able to adapt quickly to change.
6.4 Strategy and Execution
A major function of EA is revealing the relationships of all the different business elements, information elements, and the underlying information technology and technology infrastructure. By demonstrating these interrelationships at a systems level down to the most detailed element or artifact level, EA provides the information needed to connect an organization’s strategy to the enablers for execution of that strategy.
Over the last several decades, enterprises of all types, whether in manufacturing, finance, HR, or systems integration, have moved from vertically integrated entities to horizontally interdependent supply chains. [15] With this movement, the ways that enterprises compete and what they create internally versus what they source externally (often referred to as make versus buy decisions) are moving from the physical elements and on-site infrastructure to applications and off-site datacenters, even in the cloud. This change started with hardware infrastructure, moved into software infrastructure, and continues into applications, information, and even specialized business functions. This makes EA even more necessary to help EIT and enterprise management see the connection between business processes and the EIT services those processes depend on.
7 The Conventional Wisdom
Three almost universally adopted concepts characterize the current state of the art of enterprise architecture:
- The four layer stack model — or the four aspects — of an enterprise
- The delineation of as is and to be states
- The use of frameworks
7.1 The Umbrella Nature of Enterprise Architecture: Layers or Aspects
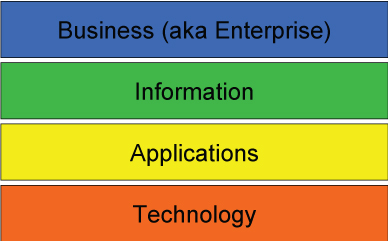
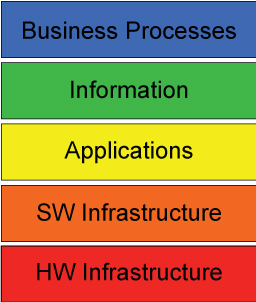
The conventional model (called the BIAT model) of an organization’s EA is sometimes represented as a four layer horizontal stack.
- Business
- Data/information
- Applications
- Technology
Figure 4 depicts a layered BIAT model.
Figure 4. Conventional BIAT Diagram (Note: In other models, the layers are not shown as horizontals; instead, they are shown as verticals, and in this view they may be called domains or aspects.)
7.1.1 Business
For the purposes of the EITBOK, business should be considered synonymous with enterprise. While it may seem odd, it is a demonstrable fact that there is no explicit definition of business that is universally or even widely shared by the EA community. Instead, the assumption seems to be that the EA community simply knows what business means. However, some sense of what the business domain is about can be inferred from the stack metaphor — it is whatever is ultimately to be supported by the technology domain.
7.1.2 Data or Information
For the purpose of the stack metaphor, information is increasingly associated with business concerns while data storage is a concern within the technology domain. The enterprise runs on information, and thus the patterns of information use by the business largely determine the data technology support needed to support those information needs.
7.1.3 Applications
Software applications consume, transform, and produce data to support the information needs of the enterprise's technology users. Often, the heaviest information "consumers" are in HR and finance units, although software increasingly supports facilities management, inventory control, etc.
7.1.4 Technology
The technology domain includes processors, storage and network connectivity, and the middleware that provide the basic computing and communications capabilities for the enterprise. They enable the flow of information that is the lifeblood of the organization. Note that the EIT technology domain thus does not typically include physical process technology such as industrial or manufacturing automation technologies.
7.1.5 Where the Action Is
It is an unstated presumption of the BIAT model
- that the transformative value of EA is typically delivered by transformation of the application and technology domains,
- that agility of the enterprise is a consequence of agility of the EIT function,
- and that alignment of the business and EIT is achieved by aligning EIT with the business.
It is common within the EA community to recognize that each of these layers has its own architecture, and that the enterprise architecture is in some sense the sum or union of these architectures. At the same time, it is also common within the EA community to say that the enterprise comprises the businesses + IT, and therefore that the enterprise architecture comprises business architecture + IT architecture, with IT architecture comprising data/information architecture, applications architecture, and technology architecture (though it is often conceded that the data/information architecture may straddle the boundary between the business and EIT domains).
The stack metaphor derives from the idea that the technology architecture is ultimately driven by the needs of the business domain/architecture (an expression of the business/EIT alignment rationale), with the data/information and applications architectures as key waypoints.
There are several different models in use for how this integration across the layers or aspects is best achieved. One of the most common is the service model, where each layer delivers services to the layers above it. Not surprisingly, the question of what exactly makes something a service remains a subject of considerable discussion within the EA community. Other models focus on the enterprise’s value chain, or enterprise capabilities.
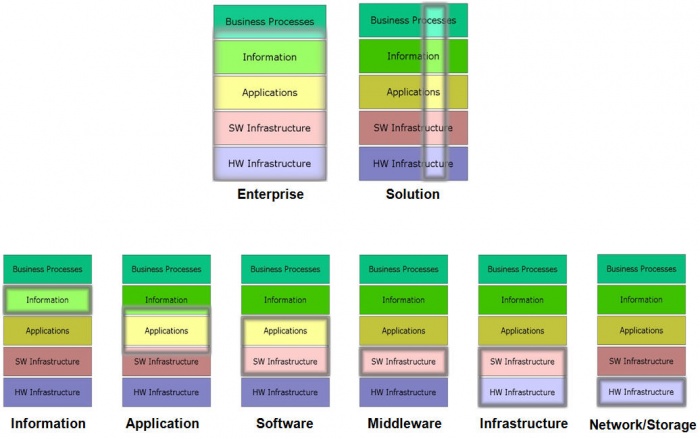
Figure 5 depicts a variation of the conventional BIAT diagram. This shows that the focus of much of EA practice is on business processes, and divides the technology domain into software and hardware infrastructure, because they are qualitatively different in nature. This diagram is used later to illustrate the relationship between EA and other enterprise-related architectures.
Figure 5. Modified BIAT Diagram
7.2 The As Is and To Be States
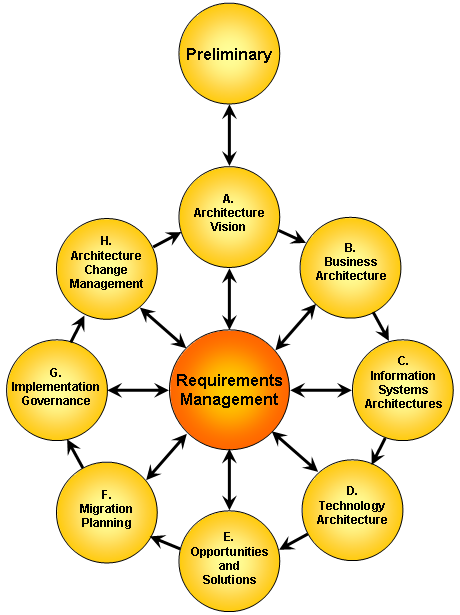
As noted earlier, EA serves a key role in organizational transformation in bridging strategy to execution. (You can’t get where you want to go unless you know where you are.) Essentially, one needs to understand the current as is state relative to the desired to be future state, identify the gaps, and chart at least a high-level plan or roadmap to get from today’s current state to the future. The Open Group describes an approach that it calls the Architecture Development Model (ADM) that consists of a number of iterative phases as shown in Figure 6. [14]
Figure 6. TOGAF 9.1 ADM Steps [14]
7.3 Evolving Frameworks
Instead of the different layers in the BIAT model, several frameworks add a second (vertical) dimension to connect the architecture aspects of BIAT with the specificities of when and how to create and use the architecture. Two examples are provided: the Zachman Framework, which is one of the first frameworks for EA, and a simpler version of Zachman, the Integrated Architecture Framework (IAF). In both examples, the layers ultimately extend from the enterprise perspective down to the technical implementations via requirements management and construction:
- Contextual — the why, the connection to the business strategy, principles
- Conceptual — the what, the service level
- Logical — the how, the logical flows
- Physical — the with what, the specific elements
Figure 7 shows a more detailed and complex framework, where the business, information, applications, and technology are vertical "domains" rather than layers. This is the Zachman Framework, and was groundbreaking at its time. [11]
Figure 7. Zachman Framework for Enterprise Architecture [11]
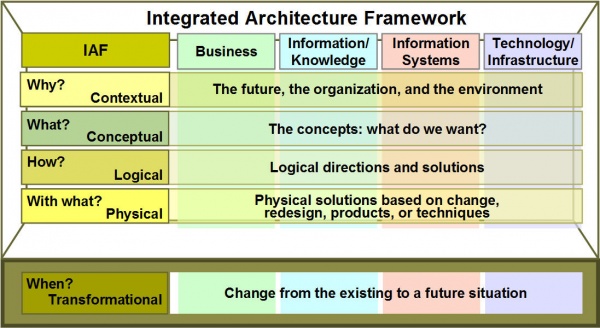
Figure 8 depicts the Integrated Architecture Framework (IAF), in less detail than the Zachman Framework illustration. [12] Here, the BIAT aspects are shown vertically, and the horizontal layers show varying degrees of abstraction from contextual (the why), to conceptual (the what or service layer), to logical (the how including processes), and, finally, at the lowest level, the physical (the with what layer). Adding the transformational (the when), it includes the dynamic dimension, from the current or existing state to the future state.
Figure 8. Integrated Architecture Framework [13]
With these layers, these different perspectives and dimensions of detail are more apparent than in the simple BIAT model.
8 The Geography of Enterprise IT Architecture and Links to Other Disciplines
Enterprise architecture is valuable and useful if it influences and integrates the inputs and outputs of other architecture disciplines in the enterprise and bridges between the enterprise strategy and the IS/EIT projects.
8.1 The Relationship between EA and Other Architectures
A recent survey conducted by the Journal of Enterprise Architecture asked survey respondents for their titles. Among the respondents who had architect in their title, there were 21 different non-level-related modifiers. Labels that architects use rather than simple enterprise architect include business process architect, information architect, applications architect, solution architect, software architect, middleware architect, infrastructure architect, network architect, network storage architect, hardware architect, and so on.
Figure 9 shows that the simple view of enterprise architecture (first introduced in Figure 5) also describes other typical architecture types. All of them must consider solution, information, application, software, middleware, infrastructure, and network storage.
Figure 9. Enterprise and Other Enterprise-related Architectures
8.2 The Relationship between Enterprise Architecture and Enterprise IT
EA serves as a bridge between the enterprise’s vision and strategy and how the underlying layers of business elements (including business processes and people) are organized, as well as the flow of information and data elements. Business processes and information are not necessarily automated with IS/IT. For example, without IS/IT automation, workers may manually take measurements, create reports, and deliver data and information in those reports. On the other hand, where business process and information flows are automated with IS/EIT, EA describes the interdependencies, and linkages between the business (organization), information, applications, and technology infrastructure.
In contrast, enterprise IT (EIT) consists of the applications and technology infrastructure supporting the applications, so nowadays EIT is increasingly seen as a subset of EA.
Distinguishing between EA and EIT is important, and by doing so, an organization should clearly recognize that there is always a choice to either support business roles, business processes, and information flows with automation (i.e., IS/EIT) or keep them manual. Likewise, the governance and influence of EA is different than the governance and influence of EIT.
Artifacts (i.e., outputs or deliverables) from EA are found as inputs to strategy and governance as well as requirements (and subsequently, construction). Here are some examples:
- Strategy maps
- Capability maps
- Information maps
- Value maps
- Heat maps
- Organization maps
- Operating models
- Product maps
- Stakeholder maps
- Process models
- Dynamic rules based routing maps
- Data models
- Network models
- Systems models
- Vitality and renewal plans
- A wide range of hybrid blueprints and models with specialty uses based on the challenge at hand
8.3 Solutions and Their Relationship to EA
There are different ways to view the landscape of the enterprise’s IT architecture. At the fundamental level, EA physical and logical artifacts describe the elements that support the organization’s operations. At a more conceptual level, there are the business, information, information technology, and infrastructure services. These can be related to an organization’s capabilities. Relatively speaking, these can be characterized in a colored heat map that uses color to represent different attributes or identify focus areas in a data set. Depending on the organization’s strategy, the capabilities that are most in need of improvement might be the first priority. Improvement/replacement costs, interdependencies with other capabilities and systems, risks of not improving, and so on are inputs to the prioritization process. The funding and governance of the improvement work (in the form of projects and programs) are strongly influenced by EA and typically overseen by a program management office (see the Change Strategy and Governance chapter). The projects and programs develop solution architectures and these solution architectures need to be compliant to and synergistic with the evolving enterprise architecture.
8.4 EA and Nonfunctional Requirements or Cross-layer Concerns
In the Requirements chapter, the two types of requirements, functional and non-functional, are discussed. While EA influences both types, its impact on functional requirements is more obvious. However, EA also influences nonfunctional requirements and can do so through the overriding EA principles as well as in what are called collaboration contracts between EA artifacts. Here are some examples.
- Business service collaboration contracts: An example would be a business service, a set of business processes like a financial operation and its expectations in receiving information data elements from a sales service (i.e., an order entry from a sales operation).
- Technology infrastructure component collaboration contracts: Technology infrastructure examples include storage components and networking components. Collaboration contracts between the two might be the quality and reliability expectations in terms of up time, error-free processing, messaging, latency, and so on.
In these contracts, the expectations of various qualities are defined and are documented in delivery projects as the nonfunctional requirements. By keeping the close association between the collaboration contracts of all the artifacts in the overall EA repository with the nonfunctional requirements in the enterprise IT portfolio of projects, the quality needs and expectations across the enterprise can be balanced.
8.5 EA and Business Architecture and BPM
The discipline of EA has evolved in parallel to the discipline of business process modeling (BPM). Clearly, the business architecture needs to be characterized and described in both EA and BPM “languages” and tools. Over the last decade, this relationship has been recognized and the companies who are developing and providing EA and BPM tools are coalescing and, in doing so, helping to bridge the gap. Likewise, the respective expert communities recognize the need and are starting to address it.
8.6 EA and Scope
It is important to note that EA does not necessarily mean across an entire enterprise. EA can be narrowed to a particular “subject of concern” and a “scope” for that concern. Enterprise can be the scope (“enterprise-wide”) and, in a different way, it can be viewed as the subject. TOGAF goes into detail about the different ways of looking at EA. Overall, remember that the organization is the definer of scopes, whether it is an extended organization, specific organization, business unit, function, department, and so on. EA is not necessarily enterprise-wide. And orthogonally, the scope can be narrowed and needs to be defined in terms of domains to be considered, such as business, information, data, application, platforms, infrastructure (software and hardware), and technology (network and storage). It may depend on whether the EA team is EIT-centric or enterprise-centric. Also, there sometimes are several EA teams working on smaller chunks that must be integrated.
9 Summary
There are three almost universally adopted concepts that characterize the current state of the art of enterprise architecture:
- The four-layer stack model — or the four aspects — of an enterprise
- The as is and to be states
- The use of frameworks
Enterprise architecture should clearly influence and be influenced by strategy and governance. Additionally, there is a strong connection to requirements. Likewise, an interdependency exists between the enterprise architecture and a solution architecture (SA) for a particular application (solution architecture is included in the Construction chapter).
Enterprise architecture can be defined by its scope and subject; it can be about an entire organization or can be narrowed down to a segment, unit, or function. So EA is scalable and can be small and incremental as well as enterprise-wide.
EA can assist in both short- and long-term enterprise improvement and transformation planning.
Successful EA functions must be able to balance high-level strategic work with tactical governance and collaboration with solution architectures in the enterprise’s IT portfolio so that the portfolio provides ongoing and clear impact and value.
A useful, practical, and functioning EA framework should have independent and modular elements, and, at the same time, be able to show an integrated and interdependent view of all of the elements.
10 Key Skills
While many large companies have defined their own sets of skills for purposes of talent management (to recruit, retain, and further develop the highest quality staff members that they can find, afford and hire), the advancement of EIT professionalism will require common definitions of EIT skills that can be used not just across enterprises, but also across countries. We have selected 3 major sources of skill definitions. While none of them is used universally, they provide a good cross-section of options.
10.1 Skills Framework for the Information Age
The Skills Framework for the Information Age (SFIA) has defined nearly 100 skills. SFIA describes 7 levels of competency which can be applied to each skill. Not all skills, however, cover all seven levels. Some reach only partially up the seven step ladder. Others are based on mastering foundational skills, and start at the fourth or fifth level of competency. It is used in nearly 200 countries, from Britain to South Africa, South America, to the Pacific Rim, to the United States. (http://www.sfia-online.org)
SFIA skills have not yet been defined for the security chapter.
10.2 European Competency Framework
The European Union's European Competency Framework (e-CF) has 40 “competencies” and is used in the EU. (http://www.ecompetences.eu/) It uses five levels of competency. As in SFIA, not all skills are subject to all 5 levels. The EU has also created a mapping between e-CF and SFIA.
E-CF skills have not yet been defined for the security chapter.
10.3 i-Competency Dictionary
The Information Technology Promotion Agency in Japan has developed the i-CD, translated it into English, and describes it at https://www.ipa.go.jp/english/humandev/icd.html. . It is an extensive skills and tasks database, used in Japan and southeast Asian countries. Like SFIA, it establishes seven levels of competencies for skills. An example showcasing the skills and tasks relevant to this chapter is given below.
11 Roles
Both SFIA and the e-CF have described profiles (similar to roles) for providing examples of skill sets (skill combinations) for various roles. The iCD has described tasks performed in EIT and associating those with skills in the IPA database.
Because there is no common definition of roles per se, however, we have selected ITIL’s roles as our reference model. The relevant ITIL roles for the activities in this chapter are given below.
*** To Be Added
12 Standards
ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010
TOGAF 9.1
13 References
[1] L. Fehskens, “Why We Can’t Agree on What “Enterprise Architecture” Means, and Why That’s OK, At Least for Now,” Enterprise Architecture Conference Europe, London June 2013.
[2] ISO/IEC/IEEE, “ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010:2011, Systems and software engineering — Architecture description,” http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=50508
[3] Federation of EA Professional Organizations (FEAPO), “Common Perspectives on Enterprise Architecture,” Architecture and Governance Magazine, Issue 9-4, November 2013, pp.11-17.
[4] M. Porter, “The Five Competitive Forces that Shape Strategy,” Harvard Business Review, January 2008, pp. 79-83.
[5] J. Lapalme, “Three Schools of Thought on Enterprise Architecture,” IT Professional, vol.14, no. 6, pp. 37-43, Nov.-Dec. 2012, doi:10.1109/MITP.2011.109.
[6] N. Malik, “Three Schools of Thought for Enterprise Architecture,” blog, 28 May 2012; http://blogs.msdn.com/b/nickmalik/archive/2012/05/28/three-schools-of-thought-for-enterprise-architecture.aspx
[7] J. Zachman, “A Framework for Information Systems Architecture,” IBM Systems Journal, vol 26, no 3, 1987, IBM Publication G321-5298.
[8] The Open Group (January 23, 2015),“A Historical Look at Enterprise Architecture with John Zachman” http://blog.opengroup.org/2015/01/23/a-historical-look-at-enterprise-architecture-with-john-zachman/
[9] The Open Group (2011),“TOGAF 9.1, Part 11: Architecture Development Method (ADM) — Preliminary Phase” http://pubs.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf9-doc/arch/chap05.html
[10] Enterprise Architecture Framework, Wikipedia, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_architecture_framework
[11] This image is copyright John A. Zachman and Zachman International®, Inc. Published with the permission of John A. Zachman and Zachman International®, Inc., www.zachman.com
[12] J. van’t Wout et al, “The Integrated Architecture Framework Explained,” Springer-Verlag, 2010.
[13] Dekker, Morsink & Partners, http://www.dekkermorsink.nl/raamwerken.htm
[14] The Open Group, TOGAF9.1 ADM Steps Reference Card
[15] C. Fine, “Clockspeed,” Perseus Books, 1998.
14 Additional Reading
Schekkerman, “How to Survive in the Jungle of Enterprise Architecture Frameworks,” Trafford
Ross Weill and Robertson, “Enterprise Architecture as Strategy,” Harvard Business School Press.